With per capita income of 31% of the EU average, Albania is last in Europe and for 2018, along with Bosnia and Herzegovina, according to new data released today by Eurostat.
However, compared to the previous year, there is a slight improvement, as the indicator increased by 1 percentage point compared to the previous year, while in 2017 it was 29%.
But in the other indicator, that of individual per capita consumption, Albania ranks last only, with 38% of the European average (Bosnia has 38%).
Montenegro's per capita income in the region comes first, with 48% of the European average, followed by Serbia (39%), Macedonia (37%).
For individual per capita consumption, Montenegro is still the top, with 58%, Serbia (48%), Northern Macedonia (41%).
For years, Albania and other countries in the region have been failing to make money in the so-called convergence process, which means faster growth with developed countries in order to get closer to their average.

The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development in a recent "life in transition" report stated that Albania could take 80 years to catch the average of OECD developed countries in the so-called convergence process.
Europe
According to Eurostat, current Individual Consumption (AIC) is a measure of household material well-being. Along Eurozone member states in 2018, per capita AIC, expressed in purchasing power parity (PPS) varied from 56% of the European Union (EU) average in Bulgaria to 134% in Luxembourg.
This data, published by Eurostat, the European Union's statistics office, is based on the revised purchasing power parity and the latest GDP and population figures.
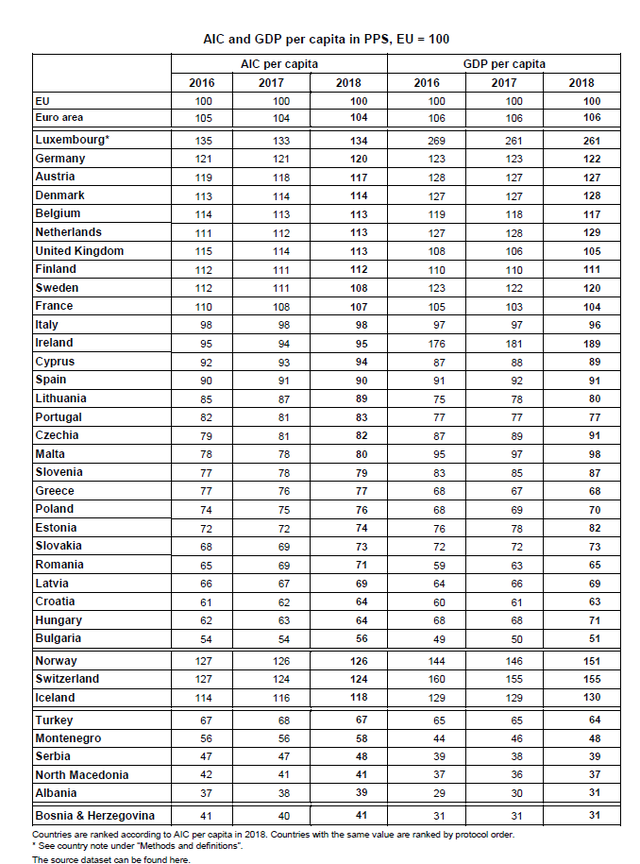
Ten member states recorded per capita consumption above the EU average in 2018. The highest level in the EU was recorded in Luxembourg, 34% above the EU average, ahead of Germany (20% above). They were followed by Austria, Denmark, Belgium, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Finland, Sweden and France with levels of 7 to 17% above the EU average.
Per capita consumption for the fourteen member states is between the EU average and 30% below. In Italy, Ireland, Cyprus and Spain levels were 10% or less below the EU average, while Lithuania, Portugal, Czech Republic and Malta were between 10% and 20% below. Slovenia, Greece, Poland, Estonia, Slovakia and Romania were between 20% and 30% below average. Four member states recorded per capita consumption of more than 30% below the EU average. Latvia, Croatia and Hungary were between 30% and 40% below, while Bulgaria had per capita consumption of more than 40% below the EU average.

Over the last three years, the per capita AIC relative to the EU average has remained relatively stable in most member states. However, significant increases have been recorded in Romania (71% of the EU average in 2018 compared to 65% in 2016), Slovakia (73% versus 68%) and Lithuania (89% versus 85%). In contrast, the most notable declines have been recorded in Sweden (108% in 2018 versus 112% in 2016) and France (107% vs. 110%).
In 2018, GDP per capita expressed in Purchasing Power Parity (PPS) ranged between 51% of the EU average in Bulgaria and 261% in Luxembourg.
Source: Monitor





