The United Nations (UN), in its projections for the Albanian population, has revised down to 30-40% expectations of how many people will remain in one country by 2100. Significant depreciation has come within a year (2019 versus 2018) and is driven by both the decline in the birth rate and the high trend of immigration.
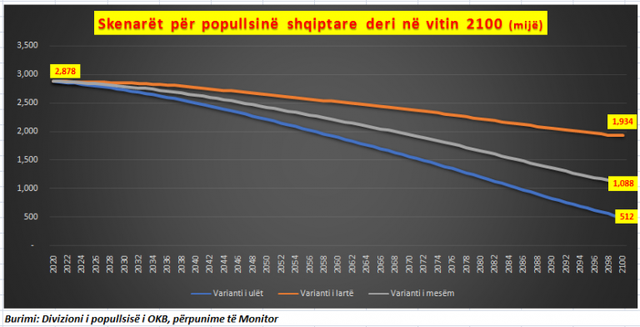
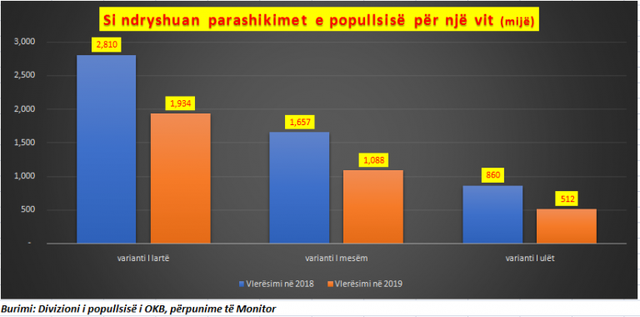
In forecasts released in 2018, according to the high forecast (high fertility rate) variant, the country's population in 2100 was expected to remain at about 2.8 million, a slight decline from the current 2.87 million. But just one year later, in 2019, expectations have dropped sharply for the optimistic variant. In all cases, even in the optimistic variant - that is, if a zero emigration rate and normal fertility rates are taken - by 2100, Albania is not expected to have more than 1.9 million inhabitants, or 31% less than forecast a year ago.
In the medium term, Albania is not expected to have more than 1 million inhabitants, up from the 1.6 million inhabitants that was forecast in 2018 for this scenario, with a decrease of about 34%.
The highest revision was made for the low scenario (high immigration rate and low fertility), according to which, in Albania in 2100, according to the expectations of the UN Population Division, Albania is not expected to have more than 512,000 inhabitants. Previously, the expectation was for 860 thousand inhabitants, so the forecast is reduced by 40%. https://www.monitor.al/parashikimi-frikshem-okb-popullsia-shqiptare-rrezikon-te-katandiset-860-mije-banore-deri-ne-vitin-2100/

reasons
The decline in fertility (fertility-gross birth rate) and the resumption of the immigration cycle are expected to shrink the population in the coming decades.
Recent INSTAT data show that women living in Albania are giving up motherhood year after year, drastically reducing the number of babies brought to life. In 2018 this phenomenon was even more pronounced when the average number of children born to a woman hit a historic record. The fertility index was only 1.37 children per woman out of 1.48 children in 2017 and out of 1.73 children per woman that was this index in 2014, according to INSTAT data.
The rapid decline in the number of births has put Albania below the replacement rate which accounts for 2.1 children per woman. Albania is also well below the global fertility rate, which in 2017 was 2.4 children per woman, according to World Bank data. Albanian women give birth to almost 50 percent fewer children than the global average.
From January 2014 to January 2018 the population of Albania has decreased on average by 0.16% per year. As a result of these developments, addiction rates have increased for older ages and decreased for younger ones. Dependency ratios are calculated by comparing the number of persons (young people 0-14 years old and / or seniors 65+ years old) with the working age population.
As of 2015, Albania is experiencing a new increase in the phenomenon of immigration. Asylum applications alone have reached about 200,000 in the last five years, according to official data from Eurostat, and there are many others who are leaving work contracts or simply leaving and not returning. Population displacement is becoming a problem for companies, which complain that they are not finding skilled labor. In a recent survey, the Albanian Institute of SMEs "SME Albania" found that about 61% of enterprises had employees leaving for immigration reasons during 2019.
The population decline, especially the removal of the working-age population, is expected to have severe effects in the future, both in the pension scheme, with the creation of a fragile layer without proper care, and with the decline in enterprise productivity, with an effect in the trend of wages, their investments and the taxes they pay, with long-term consequences in slowing the country's economy.
Source: Monitor





