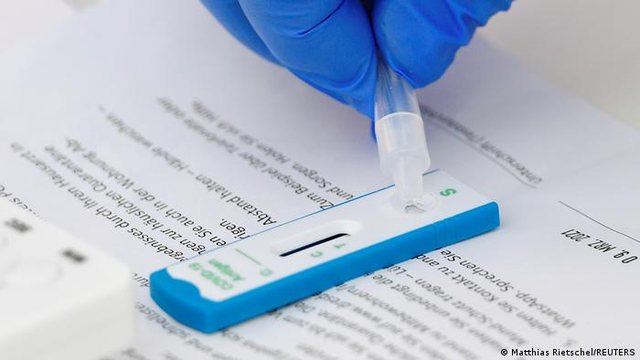
False certainty: During a check for the accuracy of rapid antigen tests for Corona detection, one in five failed the test. Manufacturers are still allowed to certify their own tests.
In the global fight against the Corona virus, rapid antigen tests play an important role not only for the unvaccinated, but in the future more and more for the vaccinated as well.
Testimi bëhet në punë, në jetën publike dhe në atë private. Nëse vlen rregulli 2G plus, atëherë të vaksinuarit e të shëruarit duhet të tregojnë edhe një test të shpejtë shtesë negativ. Shumë vetë u besojnë testeve të shpejtë që janë në përdorim nga viti 2021 dhe që ndihmojnë zbulimin e shpejtë të virusit.
Shumë vetë testohen vetë, përpara se të vizitojnë të afërmit e moshuar, apo nëse marrin pjesë në festime private.
Por kjo ndjesi e sigurisë mund të dalë e gënjeshtërt.
Studiues të Institutit Paul Ehrlich, atij Robert Koch dhe Berliner Charite morën nën lupë një numër të madh testesh antigjen që janë në përdorim. 20% të testeve nuk e kaluan kontrollin, sepse edhe kur personi kishte në vete një sasi të madhe virusi ata nuk e zbuluan.

75 e rasteve duhet të identifikohen
Sipas studimit të publikuar paraprakisht si “preprint”, publikim para ekspertizës kualifikuese, 26 nga 122 teste të shpejta që u morën në shqyrtim nuk e plotësonin kërkesën minimale: identifikimin në 75% të rasteve të virusit.
Testet duhet të zbulojnë 75% të rasteve, nëse prova e marrë ka sasi virusi. Se sa duhet të jetë sasia e virusit përcaktohet nga vlera e quajtur Ct. Kjo vlerë të orienton, se sa shpesh një provë duhet të shumohet në laborator deri sa të provohet gjeni i SARS-CoV-2. Sa më e ulët kjo vlerë, aq më e madhe sasia e virusit.
Nëse kjo vlerë qëndron në 25 atëherë sasia e virusit është shumë e lartë: Do të thotë ky person mund është shumë infektues. Nëse kjo vlerë qëndron nga 30-36 atëherë sasia e virusit është mesatare. Pozitive është, se tek një sasi e madhe e virusit rreth 80% e testeve ishin të saktë. Dhe 60% e tyre zbuluan madje të gjitha provat me infektim të lartë. Por megjithatë çdo i pesti test nuk identifikoi virusin.
Pse janë testet PCR më të besueshëm?
Si tek testi antigjen edhe ai PCR merren të njëjtat prova, sekrecione të rrugëve të frymëmarrjes si nga hunda apo grykët. Tek testet e shpejta në këto prova kërkohet për antigjene, pra për proteina të caktuara në mbulojën e virusit.
But if the test has few viruses, for example, when the person is at the beginning or end of an infection, or because he drank a lot before taking the test, then quick tests are no longer as accurate. If the test is positive, a PCR test should be performed immediately. Because in this test with the help of a polymerase chain reaction, PCR is required in the laboratory for DNA of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and here even small amounts of the virus are enough to give a positive test result.

Who verifies the accuracy of rapid tests?
The answer may surprise you: Manufacturers are still allowed to launch rapid antigen tests without external quality verification and can certify themselves on the basis of the declaration of conformity (CE) which indicates that the product meets EU requirements. The Paul Ehlrich Institute says: "According to current EU regulations on in vitro diagnostics (IVD) which currently govern the marketing authorization of IVDs in Europe, manufacturers can certify their COVID-19 tests as 'IVD'. low risk ”and abandon an independent control body before bringing them to market.
Manufacturers thus prove to themselves that their tests reliably detect antigens. An inadmissible situation, but that will change only in May 2022, writes the German institute. "Then, according to the IVD regulation, for their certification, an EU reference laboratory and another institution should be considered, because the tests should belong to the highest degree of risk. In the future this requires laboratory verification and independent data control.
Are quick tests invalid?
No way! They are important and help alleviate the pandemic because often times they detect infections and can thus help break the chains of infection. Especially when someone has a large amount of virus, they sound the alarm. But even with a negative test you can happen to be infected and infect others. Two days before you show the first symptoms you can be contagious. For this reason it is better not to sleep on laurels even after negative test results, but to be careful./DW/





